Mental health conditions are major contributors to the disease burden globally (14%).The World Health Organization in 2002 reported estimates that depression affects about 154 million people while schizophrenia affects about 25 million globally. Mental disorder is sometimes believed to be incurable which can cause delay or prevention for help seeking and can be damaging.

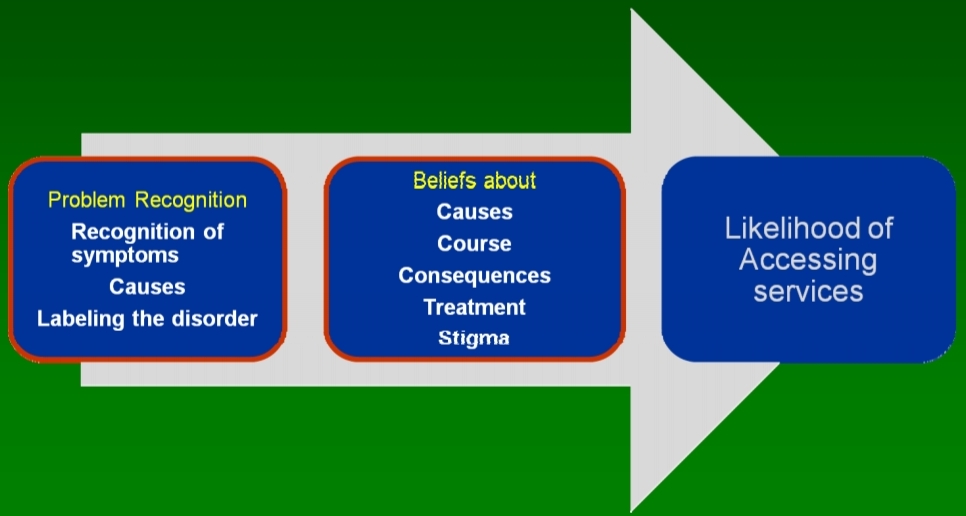
Research on mental health literacy in various parts of the globe among adolescents and young adults showed that about half of them aged 12–25 years identified depression correctly and about a quarter identified psychosis. Mental health literacy has related components including recognition and identification of mental health disorders and help seeking, knowledge on prevention of mental disorders, strategic knowledge about seeking self-help, knowledge regarding treatment and skills on how to provide support and first aid to others.
Mental health literacy in developing countries
According to an article published by KA Ganasen, S Parker, CJ Hugo, DJ Stein, RA Emsley and S Seedat Mental health is an issue of major concern in both the developed and developing world. With a lifetime risk of more than 25% for any psychiatric disorder, most people are either directly or indirectly affected. In fact, psychiatric disorders are estimated to account for 12% of the global burden of disease, yet the mental health budgets of most developing countries constitute a very small fraction of total health expenditure. In the World Mental Health (WMH) Survey conducted in 14 countries (6 less developed, 8 developed), as many as 50% of serious cases of mental illness in developed countries and 85% of serious cases in less developed countries had received no treatment in the preceding 12 months. The situation would be even worse in less developed countries.
Beliefs about causation and experience may influence patients’ beliefs about effective treatment and may also determine the type of treatment that is sought. Recognition of mental illness is an important determinant of treatment-seeking behavior, because to be mental health illiterate does not only mean that one has little or no evidence-based knowledge of mental illness or of treatment but may also mean that the knowledge and beliefs held may be derived from other sources, such as superstitions or cultural and personal beliefs
Mental health literacy in India
The prevalence of mental health conditions in India is at about 18–207/1000 population while about 2–3% are known to suffer from major mental illnesses. Less than a third of the adolescents in India could clearly identify depression (29.04%) while identification of schizophrenia was even lower at (1.31%).On assessing help seeking for mental health conditions, about 30.68% of the adolescents preferred not to seek help for possible mental health conditions with preferred sources of help being largely indicated as the mother. Professional help was relegated more for others than for self. The poor need for help seeking for mental health conditions could be an important indicator of the stigma related to mental health conditions reflecting the deeply entrenched attitude toward mental literacy in Indian society. The attitude that mental conditions should not be brought out into the open is reflects the deeply pervasive perceived stigma against mental health conditions in society. Studies indicate that mental health literacy in India is lower than average.